
As we'll see later, it is commonly renamed to main these days. It is really just a label that points to a specific commit.Īs you make new commits, Git repoints the branch name to the new commit, so a branch is basically a ref (label) that always points to the tip of the chain of commits you're working on.Īll Git repositories in which at least one commit has been made have at least one branch, which is named the master branch by default. Each of the commits in a branch references its parent commit, except the initial commit, which has no parent commit.Ī Git branch is really more of a concept than an actual data structure.
#Git list branches series#
In Git, a branch is a label that identifies a series of commits that are connected to each other.
#Git list branches how to#
In this article, we'll explain what a branch is in Git, how to create and delete branches, and different strategies for working with Git branches. To work effectively an understanding of git branches is required.
#Git list branches code#
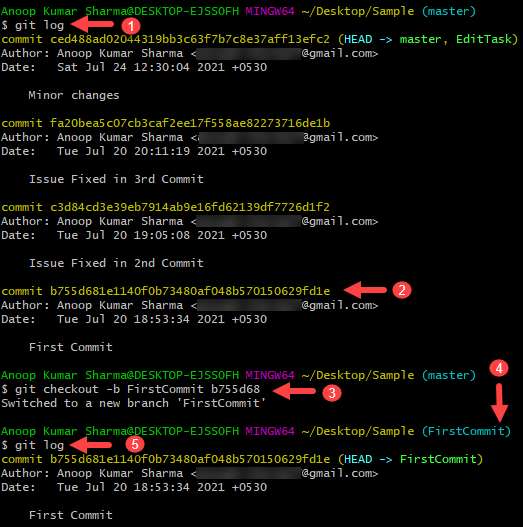
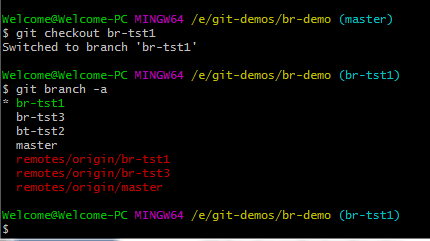
Users can obtain the hash code corresponding to the point at which the new branch will begin. The git log command displays all commits made along with their hash code. Git includes the ability to create a branch from a specific commit.Įach commit has its own hash code. There is a possibility that the master branch is not stable after a commit and a developer needs to branch over to a stable version for the new feature. Master Create a git branch based on a specific commit point: Switched to branch myrepository]# git branch The following example demonstrates how to switch from master to branch1. If a user makes changes and commits them, they will appear in branch1 only and the head of branch1 will be moved, but the master will still point to the original head. The current working branch is master, the git checkout command changes control to another branch. myrepository]# git branch myrepository]# git branchĪs you can see, there are two branches, master and branch1. With the git branch command, we will create a new branch named branch1 and again list branches. Till now only the master branch is present. List down all branches.Ĭheck to see if there is an existing branch. Remote: Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) Remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. # git clone empty Git repository in password: We have our central codebase on machine 192.168.1.159. Clone the repository.īring the copy of the central git repository on the local machine using the git clone command. We’ll assume that we’ve created a repository with git init and have access to a master branch. How can i create a branch in git? Step-by-step examples? NOTE: There can be further branching from a branch. once the new branch’s development finishes, it is merged into the mainline and removed. The Mainline continues to progress as well, with more commits being made in the mainline. Management involves creating new branches, merging existing ones, deleting them, and listing them. Along with creation, git provides a complete branch management cycle. The master branch is created after the repository is created in git. You can create another branch from an existing one, perform commits, merges, and pushes, and so on. What you can do with a branch?Ī branch has the same capabilities as the mainline. Consider it as a program’s thread that has access to all global data but has its own execution stack. Git maintains code references that are valid for specific branches.
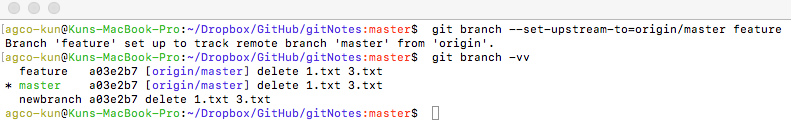
At first glance, it may appear as though that branch is simply a copy of the complete code, but it is not.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
